How Semaglutide Shapes the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: An Investigation of Its Unique Mechanism of Action
You might have heard about semaglutide as a prevalent therapeutic option for managing type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. But have you ever wondered how exactly this medication works within your body? Understanding its mechanism of action provides valuable insights into its effects and potential implications for patient care.
Semaglutide: An Overview
Semaglutide, a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist, has emerged as an essential medication for managing type 2 diabetes and obesity. By augmenting incretin function, semaglutide offers impressive therapeutic benefits. The availability of semaglutide in two formulations—subcutaneous injection and oral tablet—provides flexibility for individualized patient treatment plans.
Understanding Semaglutide’s Mechanism of Action
GLP-1 Receptor Activation
The mechanistic potency of semaglutide lies in its action on the GLP-1 receptor. As a GLP-1 receptor agonist, semaglutide binds to these receptors, leading to enhanced insulin secretion, a glucose-dependent process. This binding also inhibits glucagon release, a hormone responsible for raising blood glucose levels.
Controlling Hepatic Gluconeogenesis
By activating the GLP-1 receptor, semaglutide suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis—a process through which the liver produces glucose. This action contributes to reductions in both fasting and postprandial glucose levels, a significant achievement in diabetes management.
Delaying Gastric Emptying
Semaglutide’s action extends to the digestive system, where it slows gastric emptying. This action decelerates the rate at which glucose appears in circulation after a meal, thus helping manage postprandial glucose levels more effectively.
Pharmacodynamics of Semaglutide
Mimicking the Action of GLP-1
Semaglutide works by emulating the action of GLP-1, a naturally occurring hormone that aids in regulating blood glucose levels. By stimulating insulin secretion and reducing glucagon secretion when blood glucose levels are elevated, semaglutide helps maintain a balanced glucose profile.
Impacts on Insulin Resistance
In clinical studies, semaglutide not only reduced HbA1c and body weight in patients with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes but also improved insulin resistance. This improvement was primarily attributed to weight loss, reinforcing the dual role semaglutide plays in managing diabetes and obesity.
Semaglutide’s Steady State and Duration of Action
Achieving Steady State
Semaglutide reaches steady state after two weekly doses, with 75% of steady state achieved after two weeks. Steady-state concentration of the oral tablet formulation is attained within 4-5 weeks.
Duration of Action
With a half-life of approximately seven days and a duration of action of 63.6 hours, semaglutide remains active in the body for up to a week following administration. This long-acting therapeutic effect further reinforces the advantage of semaglutide over other GLP-1 receptor agonists.
Superiority over Other GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Semaglutide distinguishes itself from other GLP-1 receptor agonists through its longer half-life. This longer duration of action enables less frequent dosing, which can enhance medication adherence—a critical aspect of chronic disease management.
Adverse Effects and Contraindications of Semaglutide
While Semaglutide is known for its effective glycemic control and weight reduction properties, potential side effects range from common gastrointestinal issues to rarer, more serious concerns like severe hypoglycemia or acute pancreatitis.
Common Side Effects
The most commonly observed adverse effects of semaglutide are gastrointestinal in nature. These can include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
However, these side effects are often temporary, diminishing as the patient’s body adapts to the medication. Educating patients about these potential reactions can greatly enhance treatment compliance and overall comfort.
Serious Adverse Reactions
In rare cases, there are some serious adverse reactions linked to semaglutide that require immediate medical attention:
- Severe Hypoglycemia: This risk heightens when semaglutide is combined with other treatments such as insulin or insulin secretagogues. Symptoms may include confusion, seizures, or even unconsciousness.
- Acute Pancreatitis: Characterized by persistent, severe abdominal pain, this condition necessitates immediate medical intervention.
- Renal Impairment: Semaglutide may affect kidney function, indicated by symptoms such as reduced urine output, swelling in the legs and ankles, and fatigue.
- Allergic Reactions: While rare, severe allergic reactions are possible, manifesting as skin rashes, itching, difficulty breathing, and swelling of the face, lips, or tongue.
- Increased Heart Rate: Some patients may experience an irregular, rapid, or pounding heartbeat.
Contraindications
Semaglutide should not be administered to patients with a personal or family history of medullary thyroid carcinoma or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2) due to potential risk of thyroid C-cell tumors. It is also advised to exercise caution in patients with a history of pancreatitis and renal disease.
Despite these potential adverse reactions, semaglutide remains a powerful tool for the treatment of Type 2 diabetes in adults. By carefully monitoring patients and promptly responding to potential health concerns, the beneficial effects of semaglutide can be significantly enhanced.
It has shown promising results in clinical trials, with significant reductions in HbA1c, body weight, and systolic blood pressure reported.
Moreover, cardiovascular outcome trials have indicated its potential role in reducing the risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, a common concern in people with Type 2 diabetes. However, further research is warranted to better understand the full extent of its benefits and risks.
Administering Semaglutide
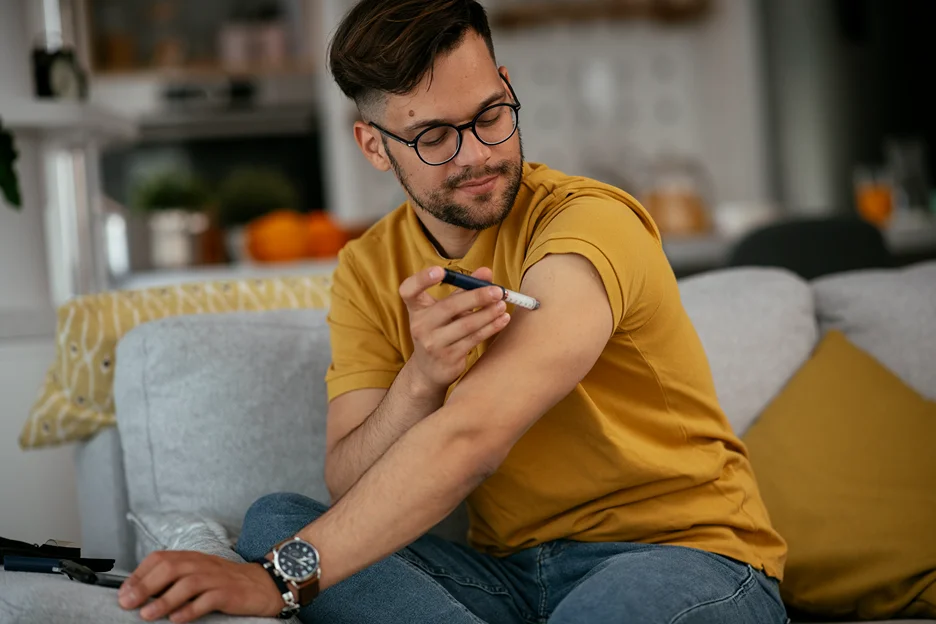

Semaglutide is typically administered via subcutaneous injection. This means that the drug is injected into the fatty layer beneath the skin, usually in the abdomen, thigh, or upper arm. The injections are usually given once weekly and can be administered at any time of the day, with or without meals.
Before injecting, it’s important to rotate injection sites within the same region to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis. The needles should be disposed of safely after use to prevent accidental needle-stick injuries or transmission of infections.
Patients receiving semaglutide injections need to be educated on the correct technique for self-administration to ensure that they receive the full benefits of the medication and to minimize potential adverse reactions.
Monitoring the Treatment Outcomes
The effectiveness of semaglutide treatment should be continuously evaluated. The primary measures of effectiveness in diabetes management include hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels and fasting blood glucose levels. HbA1c gives an indication of blood sugar control over the past 2 to 3 months, whereas fasting blood glucose gives an immediate snapshot of blood sugar levels.
Weight loss should also be tracked in patients using semaglutide for obesity management. This can be assessed using body mass index (BMI) and body weight measurements, and by noting any changes in waist circumference.
Regular monitoring of kidney function is also recommended, as semaglutide may affect renal function. The patient’s general well-being, including side effects, should also be continuously assessed throughout treatment.
The goals of treatment and monitoring plans should be individualized based on the patient’s specific needs, risk factors, and potential side effects. Ongoing patient education and engagement in their own care are crucial for achieving optimal results.
Kickstart Your Weight Management Practice with Confidence!
Do you want to incorporate weight management services into your practice but find yourself pressed for time? You’re not alone!
Join the thousands of professionals who have successfully expanded their services with this game-changing course: Implementing Semaglutide and Tirzepatide into your Aesthetic Practice.
Nikki Plourde, NP-C, a Family Medicine Nurse Practitioner with nearly a decade of experience, is here to guide you through the process in just one hour!
Nikki has been prescribing Ozempic since it first hit the market in 2017 and quickly integrated the recently-approved Wegovy into her aesthetics practice. The result? A bustling, successful practice without spending a dime on marketing! Intrigued by her success, others sought her guidance, leading her to start training others in April 2022.
Over the past year, Nikki has helped over 200 practices build their own successful weight management programs. Now, she’s ready to help you do the same!
With this comprehensive program, you’ll receive:
- A detailed PowerPoint presentation: This recorded presentation covers everything you need to know about weight management. Refer back to it as often as you need!
- In-depth knowledge: Understand the history of weight management medications, safety of prescribing (including contraindications, mechanism of action, side effects, dosing, monitoring/labs), dosing conversions, and more.
- Practical skills: Learn how to order medications online, business/marketing ideas, cost breakdown & ROI, and conducting initial and follow-up visits.
- Useful resources: Get sample copies of protocols, consents, SOAP notes, patient questionnaires/handouts, and medication safety sheets.
- Special offer: Mention our name when purchasing and receive group rate pricing for semaglutide!
This all-in-one solution, complete with the option for ongoing one-on-one support, is here to ensure your success. Don’t miss this opportunity to confidently expand your practice’s services – Enroll Today!