Mastering Medication Management: Identifying the Contraindications for Semaglutide in Patient Care
As nurses, one of the critical aspects of the job is to provide comprehensive information to patients regarding their treatment. Understanding contraindications, or situations when a particular drug should not be used, is crucial in this context.
This article will extensively discuss the contraindications of Semaglutide, a medication commonly prescribed for managing type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Understanding Semaglutide
Semaglutide is a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist primarily used in treating type 2 diabetes and chronic weight management. This class of drugs works by imitating the actions of the GLP-1 hormone, which regulates blood sugar levels and appetite.
Yet, while Semaglutide offers promising results in glycemic control and weight loss, it’s essential to understand that this medication may not be suitable for everyone. Certain clinical conditions may exacerbate the potential risk of adverse reactions, warranting a thorough consideration of these factors before initiating treatment.
Key Contraindications of Semaglutide
When considering Semaglutide as a treatment option, it is crucial to understand both its contraindications and potential side effects. Certain conditions strictly forbid the use of Semaglutide due to possible adverse impacts.
Here, we dive deeper into these restrictions and outline the related side effects of this medication.
Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma and MEN 2
Semaglutide is not suitable for individuals with a personal or familial history of Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC) or Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2). The root of this contraindication lies in studies conducted on rodents, where Semaglutide was shown to induce thyroid C-cell tumors. It’s worth noting that these specific thyroid C-cells play a key role in hormone production, particularly calcitonin, which helps regulate bodily calcium levels.
Hypersensitivity
Patients who have experienced allergic reactions to Semaglutide or any of its components should abstain from its use. Allergic reactions can present in various forms, from mild skin reactions such as rash and itching to severe life-threatening conditions like anaphylaxis.
Pancreatitis
The use of Semaglutide is contraindicated in patients with active pancreatitis or a history of pancreatitis unrelated to diabetes. This is due to the documented capability of Semaglutide to cause inflammation of the pancreas, a severe condition that can lead to a range of complications, including death.
Kidney Disease
Patients with acute or worsening kidney disease are advised against Semaglutide. Considering the drug’s mode of action and excretion process, patients with impaired renal function may experience intensified adverse reactions to Semaglutide.
Uncontrolled Hypothyroidism
For patients with uncontrolled hypothyroidism, Semaglutide should be avoided. Hypothyroidism can result in a range of symptoms, such as fatigue and weight gain. Given Semaglutide’s potential effects on thyroid hormone production, it is deemed unsuitable for these individuals.
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding
Due to the limited safety profile for pregnant and breastfeeding women, Semaglutide is contraindicated in these groups. It is known to cross the placenta, and its potential impact on an unborn baby remains unclear. Similarly, the drug can be present in breast milk, and its effects on a newborn are not fully understood.
Adverse Reactions and Side Effects of Semaglutide
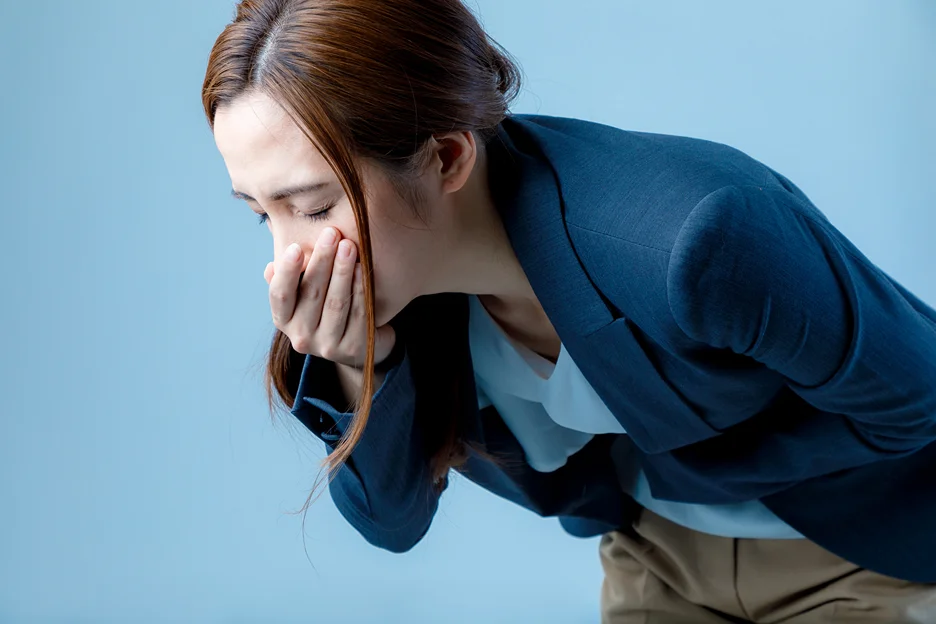

As healthcare providers, we need to be cognizant of the potential side effects and adverse reactions associated with any medication we administer, including Semaglutide. This knowledge helps us provide appropriate patient education and respond swiftly to potential health concerns.
Common Side Effects
Semaglutide’s most commonly reported side effects involve the gastrointestinal system. These typically decrease over time and include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
Educating patients about these potential symptoms and providing advice on how to manage them can significantly improve treatment adherence and patient comfort.
Serious Adverse Reactions
While less common, some serious adverse reactions require immediate medical attention. Instruct your patients to report immediately if they experience any of the following:
- Severe Hypoglycemia: When Semaglutide is used in conjunction with insulin or insulin secretagogues, the risk of severe hypoglycemia increases. Symptoms may include confusion, unconsciousness, and seizures.
- Acute Pancreatitis: This presents as severe and persistent abdominal pain. Pancreatitis is a serious, potentially life-threatening condition that requires immediate medical attention.
- Renal Impairment: Although rare, Semaglutide could affect kidney function. Symptoms include reduced urine output, swelling in the legs and ankles, and fatigue.
- Allergic Reactions: Severe allergic reactions to Semaglutide are rare but can occur. Symptoms include skin rash, itching, shortness of breath, and swelling of the face, lips, or tongue.
- Increased Heart Rate: Some patients may experience a rapid, pounding, or irregular heartbeat.
Risk Mitigation and Patient Education
Patient education is a crucial component of risk mitigation. Patients should be instructed on how to self-monitor for these side effects and understand when to seek immediate medical help. Regular check-ups and open communication lines can ensure the patients’ safety and efficacy of the treatment.
It’s important to bear in mind that while Semaglutide can have side effects, the medication’s benefits in managing type 2 diabetes or aiding weight loss often outweigh these potential risks for most patients.
As always, patient treatment should be individualized, considering the patient’s unique medical history, lifestyle, and therapeutic goals.
Proper Administration of Semaglutide
The process of administering Semaglutide can be broken down into several key steps:
- Preparation: Unpack a new Semaglutide pen and check the expiry date. Remove the pen cap and attach a new needle.
- Priming: This is an important step to ensure that the pen is ready for administration. Turn the dose selector until it reaches 0.25 mg (for the first dose). Hold the pen pointing upwards and tap lightly with your finger to push any air bubbles to the top.
- Dose selection: Each pen contains enough Semaglutide for multiple doses. Make sure the right dose is selected for each administration.
- Administration: Clean the injection site with alcohol, pinch a fold of skin and insert the needle at a 90-degree angle for most people; a 45-degree angle may be used for thin individuals. Push the dose button until you cannot push anymore. Keep the needle in the skin for 10 seconds before removing it to ensure the full dose has been administered.
- Post-administration: Safely dispose of the used needle in a sharps container. Store the Semaglutide pen without a needle attached.
Monitoring the Effects of Semaglutide
Monitoring the effects of Semaglutide is an essential part of a patient’s health management, as it allows for the assessment of the medication’s effectiveness and detection of any potential side effects.
Key aspects to monitor include the patient’s weight and Body Mass Index (BMI). Regular weigh-ins can provide a clear picture of the patient’s progress towards weight loss goals and reveal changes in BMI over time.
For patients with diabetes, it is also critical to track Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) levels, as this can indicate how effectively Semaglutide is helping to control their blood sugar levels.
As significant weight loss can lead to changes in blood pressure, regular monitoring of this vital sign is important to ensure the patient’s cardiovascular health is maintained.
Additionally, monitoring the patient for any potential side effects of Semaglutide, including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or signs of allergic reactions, enables early detection and management of these adverse events.
Together, these measures form a comprehensive approach to monitoring the health of patients on Semaglutide therapy.
Clinical Efficacy of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists: A Comparative Overview
In the clinical management of type 2 diabetes and obesity, understanding the therapeutic efficacy and safety of various medications is essential.
Among these, GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have emerged as key players, given their ability to effectively lower A1C levels, reduce weight, and maintain a low risk of hypoglycemia.
Semaglutide, available in oral and subcutaneous formulations, is a notable member of this class. As nursing professionals, understanding the comparative merits of these drugs helps in better patient management and consultation.
To provide a clearer picture, below is a comprehensive comparison table showcasing the key characteristics of some commonly used GLP-1 RAs, including Semaglutide.
Comparison of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
| GLP-1 RA | Administration | Reduction in A1C | Reduction in Body Weight | Common Side Effects |
| Semaglutide | Oral or Subcutaneous | High | High | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea |
| Liraglutide | Subcutaneous | Moderate-High | Moderate | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea |
| Exenatide | Subcutaneous | Moderate | Moderate-Low | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea |
| Dulaglutide | Subcutaneous | Moderate | Moderate | Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea |
Enhancing Your Aesthetic Practice: Integrating Semaglutide and Tirzepatide
As the field of aesthetic medicine continues to evolve, clinicians are seeking innovative ways to expand their service offerings and improve patient outcomes. Understanding and leveraging the potential of weight management medications, such as Semaglutide and Tirzepatide, can play a crucial role in fulfilling this objective.
Here, we introduce a comprehensive course titled “Implementing Semaglutide and Tirzepatide into your Aesthetic Practice“
Course Overview
Designed and led by the experienced Nurse Practitioner Nikki Plourde, who has an extensive background in Family Medicine and a successful track record with weight management medications, this course aims to equip practitioners with the skills and knowledge to integrate these medications seamlessly into their practices.
Participants of this course can expect to gain:
- In-Depth Knowledge: Learn about the intricacies of Semaglutide and Tirzepatide, including their mechanisms of action, side effects, contraindications, dosage guidelines, and necessary monitoring procedures.
- Comprehensive Curriculum: An immersive online curriculum provides vital insights through a recorded PowerPoint presentation.
- Dosage Conversion Guidelines: Receive guidance on converting doses between Semaglutide and Tirzepatide, ensuring optimal patient outcomes.
- Practical Procurement Techniques: Understand how to acquire these medications through a practical online demonstration.
- Business and Marketing Strategies: Leverage advanced strategies to boost your practice, complemented by a detailed cost analysis and evaluation of potential return on investment.
- Patient Consultation Protocols: Learn how to conduct effective patient consultations and follow-ups, including the use of pre-appointment questionnaires.
- Useful Templates: Gain access to ready-to-use templates for protocols, consent forms, SOAP notes, patient handouts/questionnaires, and drug safety sheets.
Embrace this opportunity to expand your practice’s service offerings and improve patient care. With Nikki Plourde’s guidance, you’ll be equipped to navigate the complexities of weight management medication use, positioning your aesthetic practice for continued success and growth.
Click Here to embark on this journey towards practice enhancement today!