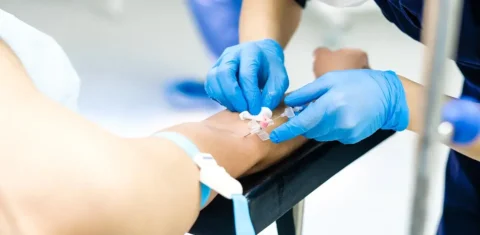
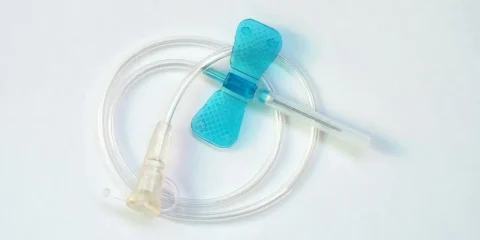
A winged infusion set is a common medical device that can be used for phlebotomy procedures. Compared to a straight needle and syringe or evacuated tube systems, a butterfly needle is smaller and allows for less painful blood specimen collection. Administering blood extraction with a butterfly needle requires you to follow the standard of draw, however, there are minimal changes in the sequence.
So what does the order of draw look like when using a butterfly needle? Normally, the blood culture tube should be filled up first. But if only a coagulation tube is needed, you should first inoculate a discard tube to remove the air in the tubing. Once you see a flash of blood in the butterfly needle hub, the discard tube can be removed and replaced with a coagulation tube or other blood bottles for specimen collection.
What Does Order of Draw Mean in Blood Collection and Why Is It Important?
Phlebotomy, or venipuncture, is a common medical procedure performed to collect an amount of blood sample from a patient’s vein. The collected blood is then sent to a clinical laboratory for testing to check a person’s vitals or diagnose a medical condition. In some cases, venipuncture is also done to remove extra red blood cells or iron.
Since a blood draw can be performed for multiple reasons, healthcare workers and phlebotomists need to follow the order of draw to make sure the right tests are done and to get accurate results. The Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) has approved a recommended order of draw to help avoid cross-contamination of additives from different blood collection tubes.
The order of draw should be followed regardless of the needle device and blood collection system being used. However, there are certain exceptions when a butterfly needle and vacuum tube holder are used for phlebotomy.
What’s The Proper Order Of Draw When Using A Butterfly Needle?
There’s not much difference in the order of draw when blood collection is done using a butterfly needle. It’s important to follow this sequence to avoid significant risks that may compromise a patient’s test result. Here’s an overview of the order of draw with a winged infusion set:
1. Blood Culture
Patients who have suspected bacterial or fungal infections usually undergo phlebotomy to detect the growth of microorganisms in the bloodstream. Normally, the blood culture tube is drawn first to prevent the risk of contamination and transmission of infectious diseases. There are two types of blood culture bottles: aerobic and anaerobic.
Whenever you’re using a winged collection set or straight needle and syringe, the aerobic bottle is filled first to avoid the transfer of air to the other tube. If air goes inside the anaerobic bottle, it may facilitate the growth of aerobic microorganisms. There shouldn’t be any oxygen inside the anaerobic bottle since it’s designed to recover microorganisms that don’t require air.
2. Coagulation or Blue Top Tubes
When coagulation testing is ordered, a phlebotomist uses a blue top tube for blood collection. This tube also contains sodium citrate which is an anticoagulant additive that prevents clot formation. This test is done to determine if a patient has serious bleeding or clotting disorders.
What Is Required When Drawing A Blue Top Tube With A Butterfly Needle?
When a butterfly needle is used to collect specimens for the coagulation tube, you should first prepare a discard tube. A winged infusion set consists of a thin hollow needle with plastic wings, transparent tubing, and a connector.
Normally, there are excess air bubbles inside the tubing and you need to remove them first or it will affect the blood volume collected in the coagulation tube. Failing to inoculate a discard tube may lead to underfilled coagulation bottles and affect the efficacy of the test result.
Why Is A Non-Additive Tube Used Before Evacuated Tube When Using A Butterfly Needle?
You should also make sure that the discard tube doesn’t contain a clot activator or anticoagulant. Avoid using other blood bottles that have an additive since this may lead to inaccurate results and interfere with the coagulation testing. Unused blood culture tubes, nonadditive serum tubes, or plastic tubes should only be used as a discard tube before collecting specimens for coagulation tests.
3. Serum or Red and Gold Top Tubes
A serum tube can contain a clot activator or gel separator for the purpose of separating the blood cells from the serum sample. Normally, this is used for clinical procedures that are done to measure hormone levels, electrolytes, magnesium, bone profile, liver function, and immunological and serological tests.
4. Heparin or Green Top Tubes
This blood collection tube can either contain lithium heparin additive or sodium heparin additive. A heparin tube is used to produce plasma or whole venous blood for certain biochemical exams, such as a red cell fragility test.
5. EDTA or Pink Top Tubes
This specimen tube contains ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) which is an additive that binds to calcium in the blood to stop clotting. An EDTA tube is filled up for tests that require hematological studies and assessment of whole blood count.
6. Sodium Chloride/Potassium Oxalate or Gray Top Tubes
This blood collection tube contains a glycolytic inhibitor to measure serum glucose and lactate levels. The additive used can either be sodium fluoride which acts as a preservative to inhibit glycolysis or potassium oxalate which prevents clotting.
Reminders for Specimen Collection with a Butterfly Needle
In addition to observing the recommended order of draw for blood collection, there are other reminders you need to follow to assure a safe phlebotomy procedure with a butterfly needle. Here are some of the important measures that you need to remember:
- Butterfly needles are best used for accessing a superficial vein. They’re also ideal for elderly patients with fragile, rolling veins that may be challenging to access with a larger needle.
- Since the winged infusion set is designed for veins on the skin’s surface, you can use a shallow angle of about 10 to 15 degrees for needle insertion.
- Always make sure to disinfect the skin prior to puncturing the skin to avoid infections.
- Blood collection tubes that contain an additive should be thoroughly inverted for a specific number of times to ensure that the substances are properly mixed. The suggested mixture of tubes: coagulation or light blue top (3 to 4 times), red serum tubes (5 to 6 times), and green and lavender tubes (8 to 10 times).
- Once the specimen collection is done, carefully pull the butterfly needle and immediately engage the safety feature to avoid sharp injuries and needlestick accidents.
- Throw the whole winged collection set in the sharps container to avoid needle reuse. Label the blood tubes properly before sending them to the laboratory for testing.
Shop High-Quality Butterfly Needles and Other Blood Collection Tools at FACE Med Store
Butterfly needles allow for a safe and convenient blood collection experience for both patients and phlebotomists. The order of draw with butterfly needles is the same as other collection systems. It’s important that you follow this protocol to assure accurate laboratory results and reduce the risk of contamination and errors in testing.
FACE Med Store has extensive experience in helping medical and cosmetic practices by providing high-quality tools and supplies. We have a selection of needles, syringes, tubes, and other necessary equipment at competitive prices. Call us today to learn more about our products or browse our site to check our stocks.