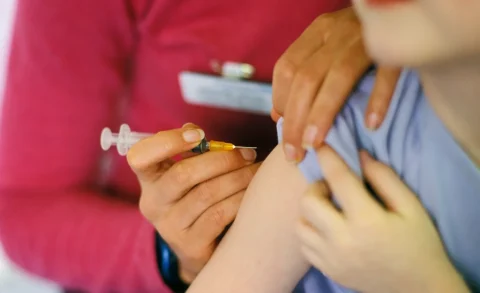
Hypodermic needles have been the delivery system of choice for many clinical drugs and medications, but they have their fair share of drawbacks. While their efficiency at directly feeding liquid treatments to the body are well-backed by science and research, using them for repeated and short-term injections can be disadvantageous to patients and medical practitioners alike.
So is there an alternative for a hypodermic needle? For procedures that require multiple treatments, dermatologists have access to one tool that works as a much better delivery system: the blunt-tip cannula.
Why Use Alternatives For Hypodermic Needles
As far as structure is concerned, hypodermic needles are relatively simple to use and understand. The needle itself is made of stainless steel tubing, with a pointed end to ensure maximum penetration into the skin. This needle is attached to a syringe or other delivery system to feed liquid treatments or drugs under the dermal layer.
The complications come after the injection has been made. Because hypodermic needles penetrate the skin, they can often cause blood vessels and arteries to burst if they breach or scratch too deeply. The deeper the injection, the more likely the dermatologist or doctor can hit a major artery, potentially causing several complications.
This problem is most apparent in dermal filler injections or other cosmetic treatments that require multiple entry sites and sessions. The skin can only handle so much trauma without bruising or marking, which can affect the results of cosmetic procedures like Botox. It can also require post-operative aftercare, which can negatively affect a patient’s quality of life.
All traditional injections run into this issue, which is why scientists have created alternative delivery systems that look to minimize pain while retaining the efficient delivery system expected of hypodermic needles.
These alternatives include MIT’s Lorentz-Force Actuator, which uses magnets and wire to propel both liquids and solids into the skin. However, these solutions still need further testing and development before they hit the market, though most clinical trials have delivered promising results.
Other scientists are also looking for ways to replace the hypodermic needle, with clinical trials for microneedles (a group of small needles that go over a patch of skin), and transdermal patches that make the drug seep into your skin. MIT in particular has experimented with manufacturing processes that can make these alternatives easier to build, like 4-D printing.
But outside of MIT and most research institutions, dermatologists can use one effective alternative to the hypodermic needle: blunt-tip cannulas. Using blunt-tip cannulas provides several advantages over traditional hypodermic needles, and can result in more efficient treatment and delivery of clinical or cosmetic drugs.
Why Use Blunt Tip Cannulas Over Hypodermic Needles
Blunt tip cannulas have one major difference compared to traditional hypodermic needles: a blunt and rounded tip. While this means that blunt-tip cannulas have no penetrating power, they make up for this drawback by being more versatile once they actually get under the skin.
Here’s a brief table outlining the major differences between the two:
| Traditional Hypodermic Needles | Blunt-Tip Cannulas |
| Sharp tip designed to pierce | Blunt tip, designed to push |
| Requires multiple entry points for different patches of skin | Needs only one entry point per patch of skin |
| Usually rigid | Can be flexible |
| Can be used for clinical and cosmetic procedures | Usually used for cosmetic procedures |
Why Use A Blunt-Tipped Cannula Over A Hypodermic Needle
Blunt-tip cannulas have found widespread success with clinical trials and cosmetic treatments, particularly with dermal fillers like Botox and surgeries like liposuction. While they’re a relatively small player in the market for drug delivery systems, their efficacy and versatility have made them the alternative of choice to traditional hypodermic needle use.
There are several advantages that come with using blunt-tip cannulas:
1. Reduced likelihood of pain
Patients are less likely to experience painful trauma to their skin since cannulas push, not pierce through the skin. Most instances of pain often occur because of the needle piercing a blood vessel or a nerve cluster – but with cannulas, painless application of drugs is possible.
2. Can be integrated with other existing medical tools
Blunt-tip cannulas are easy to integrate with other medical devices like syringes and medical tubing. This makes it relatively easy for medical and cosmetic practices to use cannulas if their patients ask for them.
THE PERFECT NEEDLES FOR YOUR PATIENTS. CODE “20OFF” FOR 20% OFF YOUR FIRST ORDER!
FACE Med Store supplies countless doctors and clinics with all their supplies, including top-of-the-line hypodermic needles. Get your hypodermic needles at 20% off today!

3. Not intimidating to patients
Patients may also be more accommodating of the design of the blunt-tip cannula. Traditional hypodermic needles have been long associated with pain and patient anxiety, which are factors that may interfere with successful treatment. Knowing that a relatively easy, efficient, and painless approach may help patients cope better with surgical or cosmetic procedures.
4. Less active trauma and post-operative bruising
Using cannulas also makes it possible to treat large patches of skin with a single injection. With traditional hypodermic needles, dermatologists would need to make multiple injections depending on how large the patch of skin they had to treat. Repeated injections on different patches of skin were more likely to cause bruising, which may require extensive postoperative aftercare.
5. A more versatile tool for the dermatologist
For dermatologists and doctors, this also cuts down the possibility of the patient moving during the procedure. A patient may involuntarily twitch or spasm during the procedure, which can be dangerous when general anesthesia is not always an option. Using blunt-tip cannulas are also a great way to avoid needlestick injuries.
When A Hypodermic Needle Is Still Best Choice
With all that said, there are still situations where using a traditional hypodermic needle is more helpful. For single-entry injection sites such as insulin injections or vaccinations, hypodermic needles are still the delivery system of choice for their efficient action and fast delivery.
Hypodermic needles excel at delivering drugs into the system with speed, which can be crucial for medications like muscle relaxants. Cosmetic procedures that target fine lines or wrinkles may also benefit from hypodermic needle use, since the speed of the results is often the best advantage of these treatments.
Get High-Quality Syringes, Hypodermic Needles, and Cannulas From FACE Medical Supply
It will ultimately fall upon the dermatologist or doctor to decide if using an alternative to the hypodermic needle is the best option. While it is a mainstay of many cosmetic and clinical procedures, an alternative approach can offer advantages that can work to improve the patient experience.
At FACE Medical Supply, we pride ourselves on providing high-quality medical tools like hypodermic needles, cannulas, and syringes at competitive prices. Visit our store page today to find out more information about our stocks and products.
Read more: Cannula vs Needle Piercing: What’s The Difference?